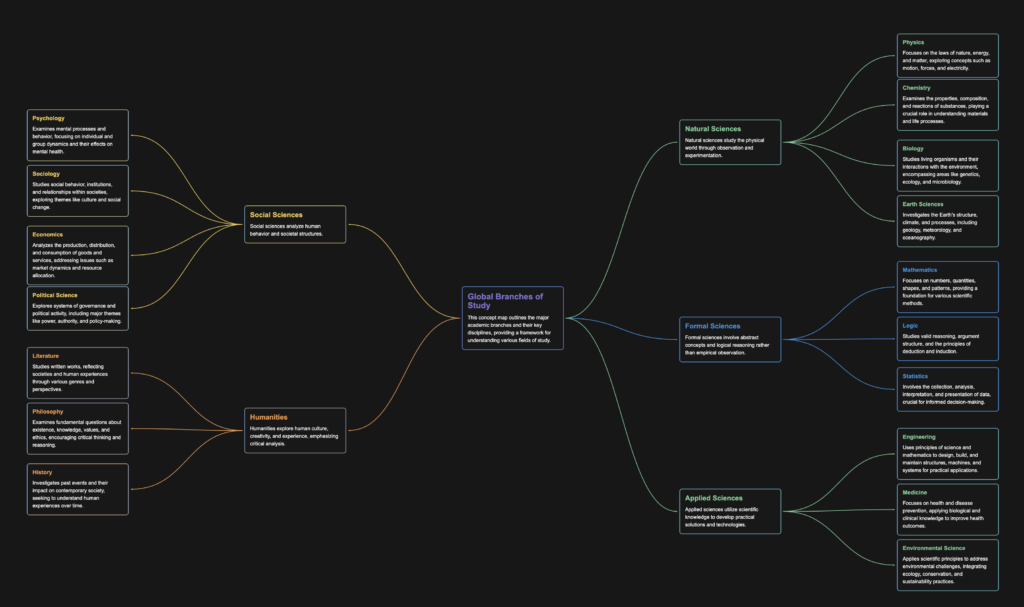
This guide provides an overview of the major fields of study, which are organised into five global branches: Natural Sciences, Social Sciences, Formal Sciences, Humanities, and Applied Sciences. Each branch encompasses key disciplines and sub-branches, representing a structured approach to understanding the world through academic and practical perspectives.
1. Natural Sciences
Natural sciences focus on understanding the natural world, encompassing both physical and biological aspects.
Key Branches:
- Physics: The study of matter, energy, and the fundamental forces of nature. Topics include mechanics, thermodynamics, and quantum mechanics.
- Chemistry: The study of substances, their properties, and how they interact. This field includes organic, inorganic, and physical chemistry.
- Biology: The study of living organisms and life processes. Sub-branches include:
- Botany: The study of plants.
- Zoology: The study of animals.
- Genetics: The study of heredity and gene function.
- Microbiology: The study of microorganisms.
- Ecology: The study of ecosystems and environmental relationships.
- Astronomy: The study of celestial bodies and the universe as a whole. Topics include planetary science, cosmology, and stellar evolution.
- Earth Science: The study of Earth’s physical constitution and processes, including:
- Geology: The study of Earth’s rocks, minerals, and landforms.
- Meteorology: The study of atmospheric processes and weather.
- Oceanography: The study of the ocean’s ecosystems and dynamics.
- Environmental Science: The study of environmental systems and human impact on nature.
2. Social Sciences
Social sciences investigate human behaviour, societies, and social relationships to understand and improve our collective experiences.
Key Branches:
- Psychology: The study of the mind and behaviour, exploring cognition, emotion, and interpersonal interactions.
- Sociology: The study of social relationships, structures, and institutions. Topics include social theory and cultural sociology.
- Anthropology: The study of human cultures, evolution, and social customs, with branches like:
- Cultural Anthropology: Focuses on societal customs and traditions.
- Archaeology: Examines human history through artefacts and remains.
- Economics: The study of production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. Sub-fields include macroeconomics and microeconomics.
- Political Science: The study of political systems, governance, and public policy. Topics include international relations and political theory.
3. Formal Sciences
Formal sciences are concerned with abstract concepts, logic, and the creation of formal systems.
Key Branches:
- Mathematics: The study of numbers, quantities, and shapes, serving as a foundation for many other sciences. Sub-branches include:
- Algebra: The study of symbols and equations.
- Calculus: The study of change and motion.
- Geometry: The study of shapes and spatial relationships.
- Logic: The study of reasoning and argumentation, essential in disciplines like mathematical logic and philosophical logic.
- Computer Science: The study of computational systems and information processing, including fields like:
- Artificial Intelligence: The development of intelligent machines.
- Cybersecurity: The study of protecting computer systems.
- Statistics: The study of data analysis, probability, and statistical inference, applicable in many fields such as social sciences, business, and health.
- Systems Science: The study of complex systems in nature and society, focusing on interdependent parts that influence the whole.
4. Humanities
Humanities explore human culture, expression, and intellectual achievements, often through critical and historical analysis.
Key Branches:
- Philosophy: The study of knowledge, reality, and existence, encompassing topics like ethics, metaphysics, and epistemology.
- History: The study of past events and human experiences, focusing on understanding cultural, political, and social developments over time.
- Literature: The study of written works, analysing prose, poetry, and drama to explore themes and human experience.
- Linguistics: The study of language and its structure, with sub-fields like:
- Phonetics: The study of speech sounds.
- Syntax: The study of sentence structure.
- Art and Art History: The study of visual arts, architecture, and cultural artefacts, exploring artistic expression and its impact on society.
- Religious Studies: The study of religions, beliefs, and their cultural significance, examining the influence of religious thought on societies.
5. Applied Sciences
Applied sciences use scientific knowledge for practical and technological advancements, often aiming to solve real-world problems.
Key Branches:
- Engineering: The design, construction, and use of machines, structures, and systems. Sub-branches include:
- Mechanical Engineering: The study of machinery and devices.
- Electrical Engineering: Focuses on electrical systems and circuitry.
- Civil Engineering: Concerned with construction and infrastructure.
- Medicine: The science and practice of diagnosing, treating, and preventing diseases. Sub-fields include:
- Surgery: The treatment of injuries and disorders through operations.
- Psychiatry: The study of mental health and disorders.
- Public Health: The study of health on a community and population level.
- Environmental Science: Applies biology, physics, and chemistry to address environmental challenges, promoting sustainable practices.
- Agricultural Science: The study of agriculture, crop production, and animal husbandry, improving food security and resource management.
- Health Sciences: Encompasses fields related to healthcare and medical technology, including nursing and physical therapy.
These five global branches of study provide a structured approach to understanding the complexities of the world, both in theoretical knowledge and practical applications. Through these fields, researchers and practitioners aim to improve human understanding and address global challenges across various domains.